ANDROID ARCHITECTURE –

Hardware Components :-
- Hardware components interact with the drivers to interact with the upper layers. When any signal is received from any end-user application, these layers convert the signal from hardware devices to soft layers. For eg. – the calling system. Same way Cameras, Wifi, Antenna, & other devices works. Mostly Android uses ARM processors.
- ARM is used to design architectures & instruction sets which then gives licenses to chip manufacturing companies. Who designs the chips for mobiles. For ex – Qualcomm sells Snapdragon which is now seen in most android devices is the popular chip manufacturing company.
- Some other companies like – Mediatek, ARM, Qualcomm Snapdragon, AMD, Nvidia, Samsung, IBM, Broadcom INC & Intel create chips especially for computers.

- ARM is the most used hardware in Android devices. For checking your Android mobile processors. Use CPU-Z applicaion : https://play.google.com/store/apps/detailsid=com.cpuid.cpu_z&hl=en_IN

- ARM is based on RISC (reduced instruction set computer) which is designed to perform millions of instructions at higher speed. Since instruction requires fewer transistors it makes them cheaper to design & produce.
- Most of the instructions are completed in one cycle, which can allow the processor to handle more instructions at the same time.
Linux Kernel :
- Linux kernel is the main component that is responsible for connecting with Android libraries, android framework, and end-user applications. Linux kernel acts like a level of abstraction (Level of Abstraction – the highest level with fewer details & lowest level with high details). It is important to note that Android runs entirely on the Linux kernel.
- For checking Linux kernel version in any Android mobile. Go to About Phone/ About Device section in settings. There you will see the Linux kernel version.

Android debug bridge (adb)
- Android debug bridge (adb) is a command line tool that enables users to access device internal files. ADB commands give a variety of commands that can help in the debugging of apps. Adb acts like a client-server program which includes three main components:-
- Client – The Client is used to interact by sending commands to adb. Here we can use the computer as a client by connecting it with a mobile.
- Daemon (adbd) – Daemon runs the command on mobile. It provides service for the objects that are running.
- Server – The server manages the communication & services between the daemon & the client. The Server runs on a background process on your mobile.
For Accessing ADB (Android Debug Bridge):-
- If you download & run the terminal emulator on non-rooted devices. Adb command will not work. As terminal emulator needs superuser permission. And superuser permission can only be granted if the device is rooted. So adb command will return with adb not found. If you run adb in recent Android versions on non-rooted devices. adb will not be found, as shown below. According to an Ethical hacking researcher of the International Institute of Cyber Security, Companies regularly update the security patches to block admin access.

- From mobile – Use the Terminal Emulator application for accessing Android shell. Download the application: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=jackpal.androidterm&hl=en_IN
- For using all features of the Android shell. Your mobile must rooted.
- Ensure that terminal emulator application is granted in Superuser.apk or Kingoroot superuser.apk
- Type adb root to get root access in a terminal emulator.

- To know the kernel version. uname -a

- ADB From computer – Download the file on your computer for accessing mobile using ADB from your computer: https://forum.xda-developers.com/showthread.php?t=2588979
- Download version 1.3. Install & run the program. Enter Y & press enter.
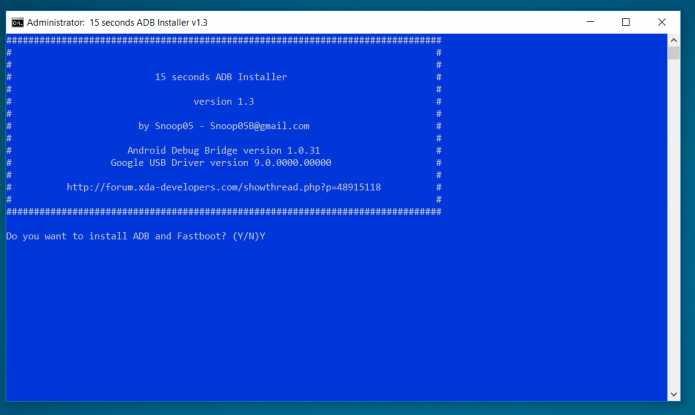
- Enter Y

- Enter Y, a popup will appear to install adb.

- Install adb & your computer will be configured to run adb shell in the Windows command prompt.
- For running open cmd as administrator.
- Connect your device with a computer. Make sure the device drivers are installed on your computer. For testing, we are using a rooted Samsung Galaxy Grand Neo Plus I9060. Download the driver for this model from: https://www.samsungusbdrivers.net/2017/02/samsung-galaxy-grand-neo-2014-usb.html
- Open CMD as administrator. Type adb devices

- Above you will see a list of available devices. You can get the kernel version of your Android mobile through a computer. Type adb shell for knowing the kernel version.

- The above screenshot shows the kernel version of your android mobile.
- Adb has a lot more features. adb is even used while developing applications.
POWER OF ADB (ANDROID DEBUG BRIDGE)
Know the Wifi Password:-
- For knowing the password of the connected wifi network.
- Enter the following command on the adb shell we got in the last steps- cat /data/misc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf Supplicant.conf stores the wifi password in plain text form.
- For security reasons, we have hidden the username & password.

- The above screenshot shows the username – ssid password – psk.
Backup Your Files with adb:-
- Type adb backup -all -f E:\backup.ab
- -all will back up all configurations of your device.
- E:\backup.ab is the backup file.
- After entering the above command. Press enter & pop-up will appear on your mobile to encrypt that file with a password. enter the password.

- Above you can see that the backup file has been saved in the desired location. You can save different files. But it will only save the configuration of that application.
- Different formats:
- .apk will only save its configuration
- .obb will save obb files.
- .shared will save SD card files.
Restore Backup Files:-
- Type adb restore E:\backup.ab

- The above file has been restored to your mobile device.
Install Multiple Applications:-
- If you want to install multiple applications on your device. Enter the following command.
- Type For %f in (E:\android_apps*.apk) do adb install “%f”

- The above screenshot shows that three applications have been installed on your device.
Copy Any Application From Your Phone:-
- First of all applications on your mobile. Enter adb shell pm list packages will list all the applications of your mobile.
- According to ethical hacking researcher, you can use them to find any spy apps on your mobile phone.

- For extracting the application type adb shell pm path com.package /data/app/com.sec.android.app.samsungapps-1.apk
- com.package– You can enter any package name.
- Enter the location of the application.
- To find the location. Open another cmd as administrator.
- Connect your device with adb. Type cd /data/app

- Then run the below command.

- For pulling out the apk. Type adb pull /data/app/com.sec.android.app.samsungapps-1.apk E:\application

- The above screenshot that the application has been pulled out from your local computer.

- Above is the application which has been pulled out from the device.
Gather Information about the device:-
- This command shows all the details of the device. Including running services, dump of blue in screen, account details & many other details of mobile.
- Type adb shell dumpsys or type adb logcat

- The above command shows a lot of information about the device. This command can be used in gathering information which can help in many phases of cyber forensics.
- For searching any particular service. For ex – Type adb shell dumpsys battery

- The above screenshot shows the information about the battery. Including its voltage with company name of the battery.
Linux Libraries/ Android Runtime:-
- Android libraries are on the top of the Linux kernel. Android libraries are responsible for playing or recording videos, and audio with defined formats. Some common native libraries like – Media, Webkit, SQLite, OpenGL, FreeType, etc. Android library consists of Java-based, C/C++ library.
- Open GL Library – It is a cross-platform application program used to create graphics.
- Webkit – It provides the function to display web content to shorten the page load.
- Media Framework – This library provides to play or to record audio & video.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) – This library is used to provide internet security.





